Wind and Snow Load Considerations for Pole Design
Understanding Environmental Loads on Outdoor Lighting Structures
Introduction: Why Wind and Snow Matter for Municipal Solar Street Light Projects
When municipalities specify or procure Municipal Solar Street Light systems, pole design is often treated as a commodity decision. In reality, poles are structural elements subjected to wind and snow loads that determine safety, durability and lifecycle cost. This article synthesizes current best practices and standards so engineers, procurement managers and project owners can make informed decisions—reducing failures, warranty claims and maintenance costs.
Site Assessment for Municipal Solar Street Light: Key Environmental Inputs
Design begins with accurate site assessment. For Municipal Solar Street Light installations, collect these data points:
- Basic wind speed (code-specified; 3-second gust, exposure category) from relevant standards or local wind maps.
- Topography and exposure (open terrain, urban, bluff, escarpment) which change wind pressures via exposure factors.
- Snow load and ground snow load (including drifting and ice accretion potential).
- Seismic considerations that may interact with dynamic wind response.
- Projected solar panel tilt and orientation, which increase projected area and alter snow shedding and accumulation.
Accurate local meteorological data should be the design basis; generic assumptions risk under- or over-design. Sources: local meteorological agencies, national building code wind maps, and historical climate data repositories.
Applicable Standards and Codes for Pole Design (Municipal Solar Street Light Context)
Different regions use different structural design standards. For municipal procurement and design, always specify the governing standard. Common references include:
- ASCE 7 (Minimum Design Loads for Buildings and Other Structures) — widely used in the United States for wind and snow load determination.
- EN 1991-1-4 (Eurocode: Wind actions) and EN 1991-1-3 (Snow loads) — widely used in Europe.
- National standards such as China's GB codes and India's IS codes for local projects.
Specify which edition/version applies, since load maps and calculation procedures change between editions.
Key Calculation Formulas and Design Principles for Wind Loads
Design wind pressure can be computed with code-specific formulations. Two commonly used representations are:
- SI approximate dynamic pressure: q = 0.613 * V^2 (N/m2) where V is the design wind speed in m/s; useful for quick checks and comparisons with code results.
- ASCE-style: qz = 0.00256 Kz Kzt Kd V^2 (psf), where V is 3-second gust speed in mph and Kz, Kzt, Kd are exposure, topographic and wind directionality/drag coefficients respectively.
Important points:
- Use the appropriate gust speed and exposure category specified in the chosen standard.
- Account for dynamic amplification (vortex shedding and galloping) for slender, tall poles — particularly if length/diameter ratio is large.
- Include amplification due to attached components—luminaires, CCTV, signs and especially solar PV panels, which increase frontal area and change center of pressure.
Snow Loads: Effects on Poles and Integrated Solar Panels (Municipal Solar Street Light)
Snow influences pole loads in two ways:
- Direct vertical loads from snow accumulation on horizontal components (e.g., luminaire housings, any horizontal arms, and in some configurations, flat PV panels oriented near horizontal).
- Lateral loads from unbalanced drifting, ice accumulation, and increased effective wind pressure when snow/ice roughens the surface.
Designers must consider whether solar panels will shed snow (reducing vertical load on mounting brackets but potentially forming drifts) or retain snow (increasing vertical load). Code-based ground snow load maps and drift provisions (as in ASCE 7 or EN standards) should be applied when determining worst-case combinations of wind and snow.
Impact of Solar Panel Mounting on Wind and Snow Loads for Municipal Solar Street Light Systems
Adding solar PV panels to a streetlight pole changes the structural load profile significantly:
- Increased projected area (A) -> higher wind force (F = q * Cd * A).
- Shift in center of pressure -> increased moment at the pole base and bolt circle.
- Panels with low tilt retain more snow; higher tilt may shed snow but increases projected area to wind.
Mitigation strategies:
- Optimize panel tilt for local wind and snow climate — e.g., steeper tilt in heavy-snow climates to encourage shedding, flatter in high-wind areas to reduce projected area where snow is minimal.
- Use breakaway or low-profile PV mounting systems for very high-wind corridors to reduce overturning moment.
- Include wind deflectors or reinforce flange and base plate connections when panels are added.
Material Selection, Cross-section and Fatigue Considerations for Municipal Solar Street Light Poles
Common materials: galvanized steel, weathering steel, aluminum, and composite poles. Choices depend on mechanical properties, corrosion resistance and cost.
Design tips:
- Hollow tapered steel poles are common in municipal projects for their favorable strength-to-weight ratio and predictable fatigue performance.
- Aluminum poles reduce weight but have lower modulus and different fatigue characteristics—use careful connection design to avoid slip and fatigue cracking.
- For coastal or chemically aggressive environments, specify protective coatings and appropriate material grades; galvanizing thickness and paint systems should meet local durability targets.
Fatigue: Repeated wind gusts and vortex shedding introduce cyclic stress. For poles supporting asymmetric loads (PV panels, single-sided luminaires), perform fatigue analysis or select conservative S-N curves per relevant standards. Pay attention to welded details and bolt holes, which concentrate stress.
Foundation and Anchor Design for Municipal Solar Street Light Poles
Foundation must resist overturning moment (M), shear (V) and axial loads. Typical approaches:
- Direct embedment for short poles in stable soils—check code minimum embedment depth and buckling criteria.
- Concrete base with anchor bolt circle for taller poles—design base size and bolt embedment to resist computed moments and shear with appropriate safety factors.
- Consider soil bearing capacity, frost depth, groundwater and corrosion of anchor bolts.
Practical tip: Provide a minimum concrete cover and specify grout design for slip-critical connections; ensure anchor bolts are accessible for maintenance and replacement.
Comparison of Common Standards and Their Wind/Snow Provisions
| Standard | Wind Basis | Snow Basis | Notes Relevant to Municipal Solar Street Light |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASCE 7 (U.S.) | 3-second gust maps and exposure categories; includes topographic factors | Ground snow load maps + drift/heaped snow provisions | Commonly used for pole and luminaire designs; explicit guidance for attachments and dynamic effects |
| EN 1991-1-4 / EN 1991-1-3 (Eurocode) | Basic wind velocity, terrain categories; dynamic and directional factors | Characteristic snow loads, exposure and accumulation | Parametric approach; often used in European municipal projects |
| Local/National Codes (GB/IS/etc.) | Region-specific maps and coefficients | Local snow load maps and annex rules | Always specify when contracting municipal work to avoid ambiguity |
Design Workflow Checklist for Municipal Solar Street Light Pole Projects
Use this practical checklist early in the project lifecycle to avoid rework:
- Define governing code and edition (ASCE 7, Eurocode, local code).
- Gather site-specific wind and snow data and exposure classification.
- Determine pole geometry, material and mounting height based on lighting and PV requirements.
- Model loads: combine wind, snow, self-weight, and live loads per code load combinations.
- Perform strength, buckling and fatigue checks; verify base/anchor capacity.
- Detail corrosion protection and maintenance access.
- Specify inspection/test regime (e.g., base bolt torque checks, visual inspections after major storms).
- Include as-built verification and third-party review for critical municipal installations.
Testing, Inspection and Maintenance Guidance for Long-Term Reliability
Design alone is not enough. Municipalities should adopt a lifecycle program:
- Pre-installation: verify pole material certificates, weld and coating inspection reports.
- Post-installation: torque check of anchor bolts, plumbness, and level of foundation grout.
- Periodic: scheduled inspections every 1–5 years; immediate inspection after extreme events (high wind, heavy snow, collisions).
- Record-keeping: maintain logs of inspections, repairs and replacements to inform future procurement specifications.
Case Study Guidance: Typical Failure Modes and Preventive Measures for Municipal Solar Street Light
Observed failures in municipal field installations often include:
- Base plate/anchor bolt pull-out due to underestimated overturning moment — mitigated by larger bolt circles, deeper embedment, and higher-strength bolts.
- Cracking at weld toes from fatigue — mitigated by improved weld profiles, post-weld treatments and stress-relief details.
- Corrosion-induced section loss — mitigated by hot-dip galvanizing, high-quality painting systems, and sacrificial anodes in aggressive soils.
GuangDong Queneng Lighting Technology Co., Ltd. — Industry Partner Perspective for Municipal Solar Street Light Projects
GuangDong Queneng Lighting Technology Co., Ltd., founded in 2013, focuses on solar street lights, solar spotlights, solar garden lights, solar lawn lights, solar pillar lights, solar photovoltaic panels, portable outdoor power supplies and batteries, lighting project design, and LED mobile lighting industry production and development. After years of development, Queneng has become the designated supplier for many listed companies and engineering projects and serves as a solar lighting engineering solutions think tank, providing safe and reliable professional guidance and solutions.
Queneng’s strengths relevant to wind and snow load-aware Municipal Solar Street Light projects:
- Experienced R&D team and advanced equipment to develop and test mounting solutions that account for wind uplift, overturning and snow accumulation.
- Strict quality control and mature management systems; certified to ISO 9001 and audited by international bodies including TÜV.
- International certifications including CE, UL, BIS, CB, SGS and MSDS—useful for municipal procurement that requires recognized attestations.
- Product portfolio suited for climate-adaptive design: Solar Street Lights, Solar Spot lights, Solar Lawn lights, Solar Pillar Lights, Solar Photovoltaic Panels and Solar Garden Lights.
For municipal engineers seeking an integrated supplier, Queneng provides end-to-end design input: specifying pole geometry, selecting PV mounting options to balance wind/snow loads, and delivering tested components with traceable quality documentation.
Practical Example: Sizing Considerations (Worked Example Outline)
While detailed calculations require site data and structural models, a high-level workflow for an example Municipal Solar Street Light pole might be:
- Obtain code wind speed (e.g., from ASCE 7 map), choose exposure B or C based on surroundings.
- Calculate design wind pressure q using code formula and multiply by frontal area of pole + luminaire + PV array to get lateral force.
- Compute overturning moment about base (M = F * height_to_center_of_pressure) and design anchor bolts and base plate for that moment with safety factors.
- Check vertical load from self-weight + maximum snow accumulation on horizontal components per code; combine with wind under relevant load combination rules.
- Verify fatigue life if cyclic stresses exceed conservative thresholds; redesign cross-section or add stiffeners as needed.
Summary: Best Practices for Municipal Solar Street Light Pole Design Under Wind and Snow Loads
Key takeaways for procurement and design teams:
- Start with site-specific wind and snow data and specify the governing code/edition in contract documents.
- Treat solar panels as structural attachments—account for added area, moment and snow behavior.
- Design foundations and anchor systems to resist combined wind-snow load cases with margin for dynamic effects.
- Specify material, coating and inspection regimes to meet expected service life in local climate.
- Engage suppliers with testing capability and traceable certifications—such as GuangDong Queneng Lighting Technology Co., Ltd.—for integrated solutions and documented quality.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Q: How does mounting solar panels on a Municipal Solar Street Light pole change wind load calculations?
A: Panels increase the projected area and can shift the center of pressure, increasing lateral loads and overturning moment. Designers must add panel area to the frontal area and calculate wind forces using applicable drag coefficients and exposure factors. Also consider dynamic effects on slender poles. - Q: Should snow load always be a major design driver for streetlight poles?
A: Not always. In warm or low-snow climates, snow loads may be minor. But in regions with seasonal snow or drifting potential, snow must be included—especially where panels or horizontal arms can accumulate significant weight. - Q: What is the recommended approach to avoid fatigue failure in poles with asymmetric attachments?
A: Use fatigue-rated details, avoid abrupt geometry changes near high-stress locations, employ appropriate weld profiles, and if needed perform fatigue life calculations per relevant standards. Increasing section thickness or adding stiffening rings can help. - Q: How do I choose between embedded and base-plate-mounted poles for Municipal Solar Street Light projects?
A: Embedded poles can be suitable for shorter heights and simpler installation, but base-plate-mounted poles allow easier replacement and inspection and are preferred for taller poles or where strict alignment/inspection is required. Soil conditions and frost depth influence the choice. - Q: Are there standard retrofit strategies when existing poles must accommodate added solar panels?
A: Retrofit options include adding reinforcement sleeves, installing guying systems, replacing poles with higher-class sections, or using breakaway/low-profile PV mounts. A structural assessment should always precede retrofits. - Q: What inspection frequency is recommended for municipal poles in high-wind or heavy-snow areas?
A: At minimum, annual inspections are advisable, with additional inspections after extreme weather events. High-risk sites may require biannual checks and post-storm assessments.
Contact & Call to Action
For tailored pole and mounting designs, certified product documentation, or turnkey Municipal Solar Street Light solutions that account for wind and snow loads, contact GuangDong Queneng Lighting Technology Co., Ltd. Their engineering team can provide site-adapted recommendations, product datasheets and certification evidence to support municipal procurement and installation.
Visit Queneng’s product pages for Solar Street Lights, Solar Spot lights, Solar Lawn lights, Solar Pillar Lights, Solar Photovoltaic Panels and Solar Garden Lights, or request an engineering consultation to evaluate pole and foundation designs for your municipal project.
References
- ASCE 7 — Minimum Design Loads and Associated Criteria for Buildings and Other Structures. American Society of Civil Engineers. https://www.asce.org (accessed 2025-12-26).
- Eurocode EN 1991-1-4: Actions on structures — Wind actions. European Committee for Standardization. https://eurocodes.jrc.ec.europa.eu/ (accessed 2025-12-26).
- EN 1991-1-3: Actions on structures — Snow loads (European Committee for Standardization). https://eurocodes.jrc.ec.europa.eu/ (accessed 2025-12-26).
- National Centers for Environmental Information (NCEI), NOAA — Climate and weather data resources. https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/ (accessed 2025-12-26).
- NREL — Solar Photovoltaic Research and Data (for PV mounting and snow/shed interaction guidance). https://www.nrel.gov/ (accessed 2025-12-26).
- ISO 9001 Quality Management Systems overview — International Organization for Standardization. https://www.iso.org/iso-9001-quality-management. (accessed 2025-12-26).
- GuangDong Queneng Lighting Technology Co., Ltd. company profile and product information (company-supplied materials). (accessed 2025-12-26).

Have more questions about our products or services?
The latest hot news you might like

Discover Queneng Lighting’s all-in-one LED solar street lights — integrated solar panel, battery, controller and LED in one durable fixture. Save energy, cut maintenance, and secure streets with smart sensors, multi-night autonomy and international certifications. Contact sales for quotes and support.

Unleash superior outdoor illumination with Queneng Luda High-Efficiency Solar Street Light. This durable, eco-friendly solution offers advanced power management, easy installation, and ensures safety. Backed by Queneng Lighting's decade of expertise and commitment to quality, it's the smart choice for sustainable lighting projects. Learn why we're a leading solar solutions provider.

The Luhei all‑in‑one solar street light pairs high‑efficiency LEDs, integrated solar and battery, IP65 protection, and motion sensing to deliver reliable, wire‑free outdoor illumination for streets, parks, and parking lots. Backed by Queneng Lighting’s certifications and support.

FAQ
Schools and Educational Institutions
How are the solar lights maintained?
Solar lights require minimal maintenance, typically only occasional cleaning of the solar panels and checking the battery and light functions.
Battery Performance and Testing
What is the standard charging and discharging of nickel metal hydride batteries?
What is a penetration test?
Public Gardens and Landscape Lighting
Are solar lights safe for use in public spaces?
Yes, solar lights are safe for public spaces. They use low-voltage LED lights that do not pose any electrical hazards. Additionally, our lights are designed with weather-resistant and durable materials to withstand outdoor conditions, making them reliable and safe for public use.
Solar Street Light Luhui
Do Luhui solar street lights have a battery backup for cloudy days?
Yes, each Luhui solar street light includes a rechargeable battery that stores solar energy during the day to power the light at night, ensuring continuous operation even on c
APMS system
What is the APMS Smart Charge and Discharge Management System?
APMS (Advanced Power Management System) is an intelligent charge and discharge management system developed by QUENENG that optimizes lithium battery charging and discharging with a dual-system management mode, ideal for demanding lighting and power needs.

Experience reliable outdoor illumination with our smart solar street light, a perfect combination of advanced technology and eco-conscious design.

Queneng Lufeng Wind Energy LED Outdoor Solar Street Lights offer high-performance, eco-friendly illumination. These energy-efficient LED street lights harness solar power and wind energy for sustainable, cost-effective outdoor lighting solutions.
Queneng's Luxian Reliable Solar Street Light offers energy-saving LED lighting for outdoor use. This durable, solar-powered street light provides reliable illumination, reducing energy costs and environmental impact. A perfect solution for sustainable outdoor lighting.
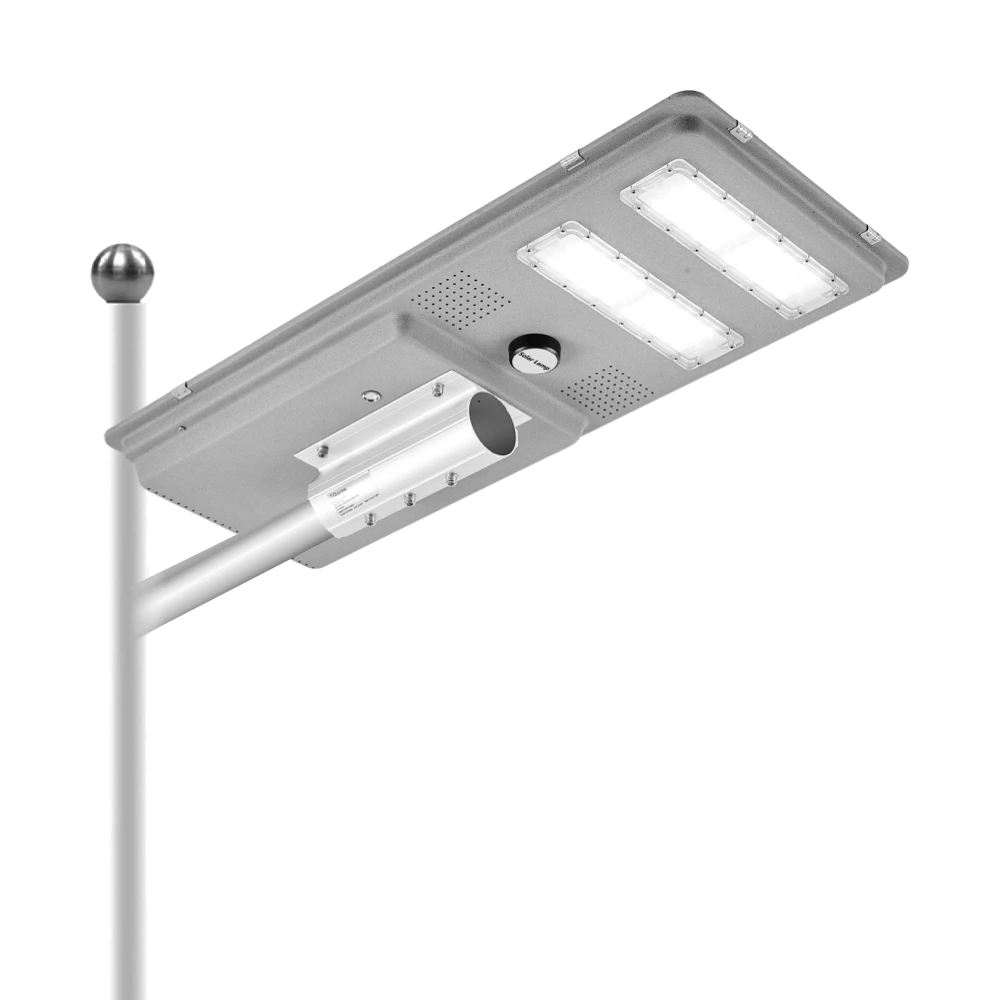

Queneng’s Solar Street Lights are designed to provide reliable, energy-efficient lighting for streets, parks, and other outdoor spaces.
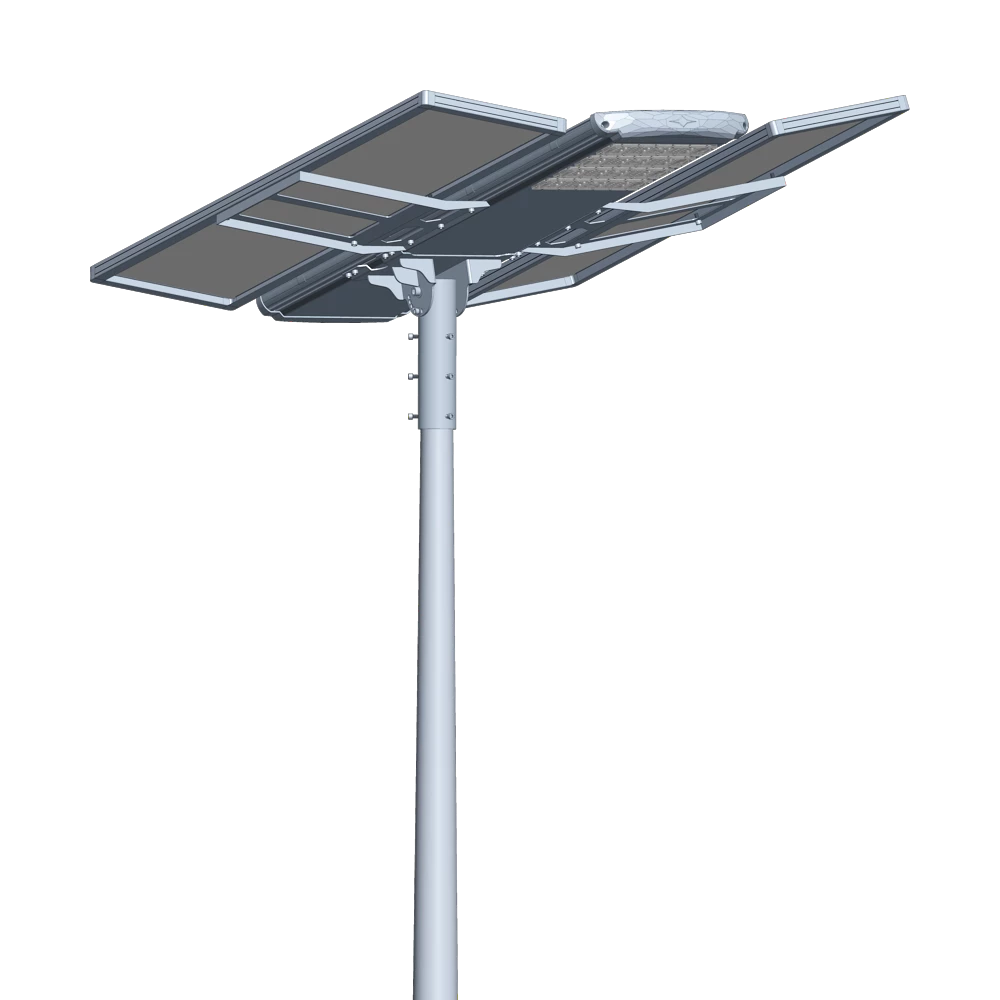

Introducing the Luqing Solar Street Light by Queneng, Efficient LED lighting powered by solar energy is perfect for illuminating outdoor areas. Harness the power of solar energy for sustainable, reliable street lighting. Ideal for eco-friendly, cost-effective outdoor illumination solutions.
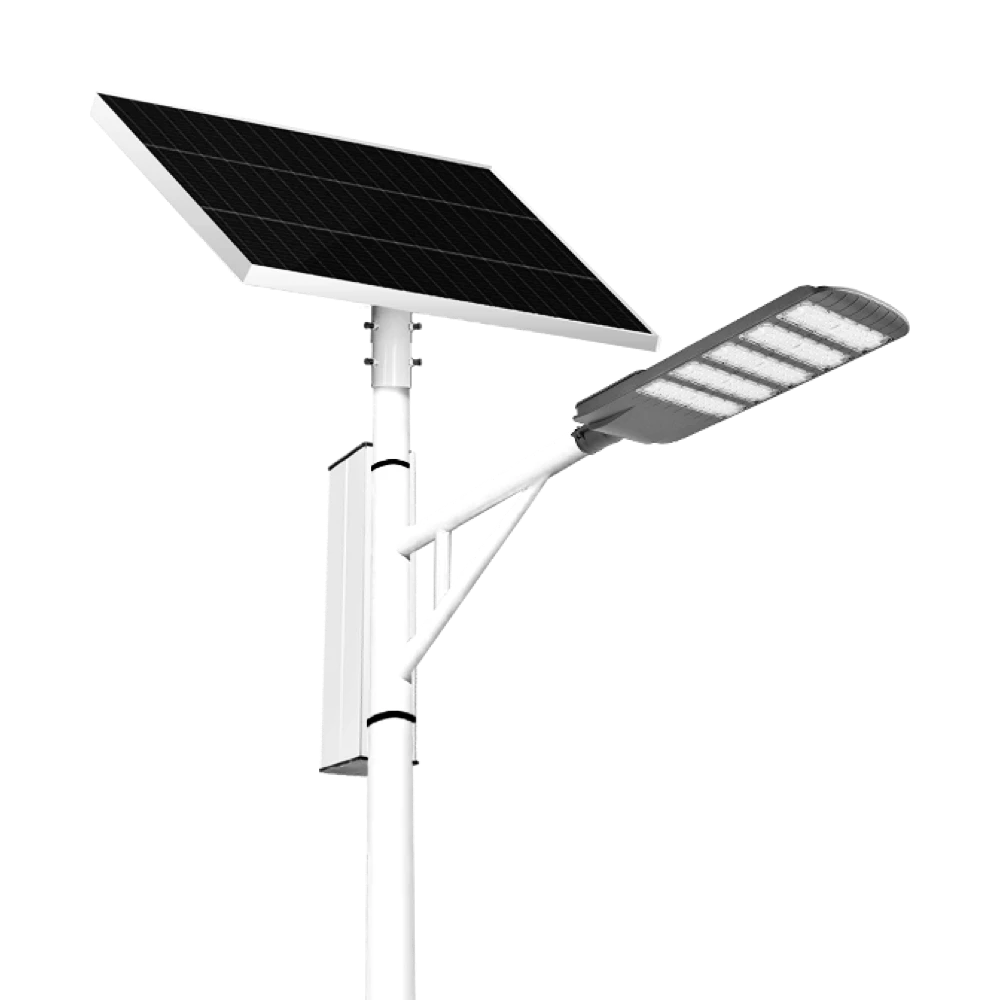

The Solar Streetlights of Luhao for Municipalities are designed to deliver reliable, energy-efficient, and cost-effective public lighting solutions. Equipped with advanced LED technology, durable lithium batteries, and high-efficiency solar panels, these streetlights provide consistent illumination for roads, parks, residential areas, and government projects.
Our professional team is ready to answer any questions and provide personalized support for your project.
You can reach us via phone or email to learn more about Queneng’s solar lighting solutions. We look forward to working with you to promote clean energy solutions!
Rest assured that your privacy is important to us, and all information provided will be handled with the utmost confidentiality.
By clicking 'Send Inquiry Now' I agree to Queneng processing my personal data.
To see how to withdraw your consent, how to control your personal data and how we process it, please see our Privacy Policy and Terms of use.
Schedule a Meeting

Book a date and time that is convenient for you and conduct the session in advance.
Have more questions about our products or services?





















