Solar Panels and Photovoltaic Power Generation Technology Overview(QUENENG)
This article provides an in-depth exploration of the development history, working principles, and current applications of solar photovoltaic (PV) power generation technology. Since the invention of the first practical solar cell in 1954, solar energy technology has undergone several breakthroughs, gradually becoming one of the key technologies in the renewable energy sector. The article explains the photovoltaic effect, the fundamental characteristics of solar cells, and the components of photovoltaic power generation systems. By analyzing the efficiency improvement trends of solar cells and the structures of different power generation systems, this article offers a comprehensive perspective on solar energy technology. Furthermore, it explores practical applications of solar power generation, including off-grid and grid-connected systems, as well as applications in residential, commercial, and other settings. Through this content, readers can gain a thorough understanding of the potential and future development of solar photovoltaic power generation.
1. Development History and Current Status of Photovoltaic Power Generation
Since the invention of the first practical photovoltaic (PV) cell in 1954, solar photovoltaic power generation technology has made significant progress. However, the development of solar energy has been slower compared to the rapid advancements in fields like computers or fiber optics. This is partly because the demand for information is particularly strong, and conventional energy sources have been sufficient to meet human needs. The 1973 oil crisis and environmental pollution issues in the 1990s greatly accelerated the development of solar photovoltaic power. Below are the key milestones in the history of solar photovoltaic technology:
- 1893: French scientist Becquerel discovered the "photovoltaic effect".
- 1876: Adams and others discovered solid-state photovoltaic effects on metals and selenium.
- 1883: The first "selenium photovoltaic cell" was made, used as a sensor device.
- 1930: Schottky proposed the theory of the "photovoltaic effect" in Cu2O barriers.
- 1954: Bell Labs developed the first practical single-crystal silicon solar cell with a 6% efficiency.
- 1962: The photovoltaic conversion efficiency of gallium arsenide solar cells reached 13%.
- 1978: The U.S. built a 100 kWp solar photovoltaic power station on the ground.
- 1990: Germany launched the "2000 Rooftop Solar Program".
- 1995: High-efficiency concentrated gallium arsenide solar cells reached 32% efficiency.
- 1997: The U.S. proposed the "Million Solar Roofs Program", aiming to install solar cells in 1 million homes.
2. Introduction to Solar Cells
Solar cells, also known as solar chips or photovoltaic cells, are semiconductor thin films that directly convert sunlight into electricity using the photovoltaic effect. A single solar cell cannot be used as a power source; several cells need to be connected in series or parallel and sealed together to form a solar panel. Solar panels are the core component of solar power generation systems and the most critical part.
Types of Solar Energy
- Solar Thermal Utilization: Solar radiation is converted into heat energy, which can be used for thermal power generation.
- Solar Photovoltaic Power Generation: Solar radiation is converted into electricity through photovoltaic conversion devices, mainly based on the principle of the photovoltaic effect.
3. Working Principle of Solar Cells
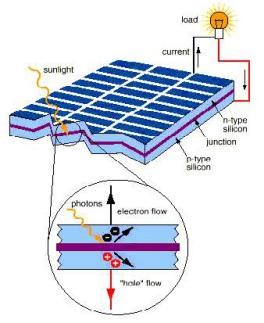
Solar cells work on the principle of the photovoltaic effect. When sunlight strikes the semiconductor material, photons with energy greater than the bandgap excite electrons and create electron-hole pairs. These non-equilibrium carriers are separated by the built-in electric field at the P-N junction, with electrons moving toward the N-type region and holes toward the P-type region. This creates an electric potential across the P-N junction. When metal leads are attached to the P-type and N-type layers and connected to an external load, current flows through the external circuit, generating electrical power.
4. Characteristics of Solar Cells
The main characteristics of solar cells include:
- Rated Output Voltage: Under standard light conditions (irradiance of 1000 W/m², temperature of 25°C), the output voltage is about 0.48V.
- Negative Temperature Coefficient: For every 1°C rise in temperature, the voltage drops by approximately 2mV.
- Power Output: The output power of solar cells varies with sunlight intensity, climatic conditions, time, and location. On sunny days around noon, the power output is close to the rated value.
5. Selection of Solar Cells
When selecting solar cells, the output power is a key factor. The standard test conditions are:
- Irradiance: 1000 W/m²
- Air Mass: AM1.5
- Cell Temperature: 25°C
These conditions roughly simulate the sunlight at noon on a clear day. In reality, the output power of solar cells will fluctuate due to variations in light conditions and environmental factors.
6. Photovoltaic Effect
The photovoltaic effect refers to the phenomenon where light causes a potential difference between different parts of a semiconductor or a semiconductor-metal combination. In solar cells, this effect is used to convert solar energy into electricity. The core principle of solar cells relies on the P-N junction, which creates an electric field that separates electrons and holes, generating voltage and thus current.
7. Solar Power Generation Systems
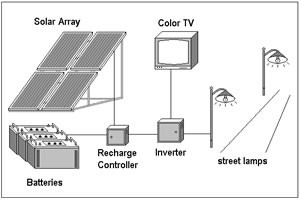
Solar power systems can be divided into off-grid and grid-connected systems. The components of these systems vary slightly:
Off-Grid Solar Power Generation Systems
These systems are used in areas without access to the grid and generally include the following components:
- Solar Cell Array: Multiple solar panel modules arranged and connected in a specific pattern.
- Energy Storage Battery: Used to store electricity for use when the sun is not shining.
- Controller: Controls the charging process of the energy storage battery and includes various protective functions to ensure safe and stable operation.
- Inverter: Converts stored DC electricity into AC electricity.
- Distribution Box and Connecting Wires: Used to connect and manage the system components and power output.
Grid-Connected Solar Power Generation Systems
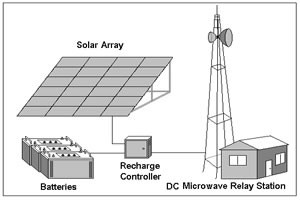
These systems are used in areas with grid access, and they can feed excess electricity back to the grid. Key components include:
- Solar Cell Array: Multiple solar panel modules connected together.
- Energy Storage Battery: Used to store electricity.
- Grid-Tied Inverter: Converts DC electricity from storage into AC electricity suitable for the grid.
- Distribution Box and Connecting Wires: Used to connect and manage the system components and power output.

Have more questions about our products or services?
The latest hot news you might like


A comprehensive 2026 guide to solar street light pricing. Covers commercial installation costs, LiFePO₄ battery trends, smart IoT features, and a detailed ROI comparison against traditional grid lighting.

A comprehensive 2026 outlook on integrated solar street lights, featuring performance benchmarks like bifacial panels, LiFePO₄ batteries, and Smart City IoT integration for maximum ROI.

Discover how solar panels power street lights, exploring the technology behind solar energy conversion, storage systems, and how solar-powered street lights are revolutionizing urban and rural lighting solutions.
FAQ
Battery Performance and Testing
What are the common charging methods?
1) Constant current charging: The charging current is a certain value during the entire charging process. This method is the most common;
2) Constant voltage charging: During the charging process, both ends of the charging power supply maintain a constant value, and the current in the circuit gradually decreases as the battery voltage increases;
3) Constant current and constant voltage charging: The battery is first charged with constant current (CC). When the battery voltage rises to a certain value, the voltage remains unchanged (CV), and the current in the circuit drops to very small, eventually tending to 0.
How to charge lithium battery:
Constant current and constant voltage charging: The battery is first charged with constant current (CC). When the battery voltage rises to a certain value, the voltage remains unchanged (CV), and the current in the circuit drops to very small, eventually tending to 0.
What is static resistance? What is dynamic resistance?
Solar Street Light Luda
What are the installation requirements for Luda solar street lights?
Installing Luda solar street lights is straightforward and does not require complex wiring. The lights come with easy-to-follow installation instructions, typically involving mounting the pole, securing the light fixture, and positioning the solar panel for optimal sunlight exposure. Since they don’t require any electrical wiring, the installation is quick and cost-effective.
Public Gardens and Landscape Lighting
Are solar lights safe for use in public spaces?
Yes, solar lights are safe for public spaces. They use low-voltage LED lights that do not pose any electrical hazards. Additionally, our lights are designed with weather-resistant and durable materials to withstand outdoor conditions, making them reliable and safe for public use.
Transportation and Highways
What maintenance is required for highway solar lighting systems?
Routine maintenance includes cleaning the solar panels, checking the battery status, and inspecting the light fixtures every 6-12 months.
Municipal and Public Infrastructure
How do solar streetlights perform in extreme weather conditions?
Solar streetlights are designed to withstand harsh environments, including high winds, heavy rain, snow, and extreme temperatures. Our products are IP65-rated for waterproofing and are built with corrosion-resistant materials.

Introducing the Luqing Solar Street Light by Queneng, Efficient LED lighting powered by solar energy is perfect for illuminating outdoor areas. Harness the power of solar energy for sustainable, reliable street lighting. Ideal for eco-friendly, cost-effective outdoor illumination solutions.
If you would like more information about Queneng solar lighting solutions, please send us a message by filling out the form below. Our professional team will get back to you within 24 hours!
Rest assured that your privacy is important to us, and all information provided will be handled with the utmost confidentiality.
Schedule a Meeting

Book a date and time that is convenient for you and conduct the session in advance.
Have more questions about our products or services?





















